AI Platform Notebooks is a managed service that provides an integration of JupyterLab, Git, and optimized data science libraries and frameworks. From it, you can get access to almost all ML frameworks, such as TensorFlow, Keras, PyTorch, etc. It is an excellent place for machine learning developers to experiment, develop, and deploy models into production. In addition, AI Platform Notebooks also supports enterprise security architectures through shared VPC and private IP controls.
What is Shared VPC?
Shared Virtual Private Network (VPC) allows organizations to connect resources from multiple projects to a common/shared VPC network. This allows cloud resources to communicate with each other securely and efficiently using internal IP addresses. Using Shared VPC is a good practice for Organization Admins to keep centralized control over network resources, while delegating administrative responsibilities to Service Project Admins.
What is the Problem?
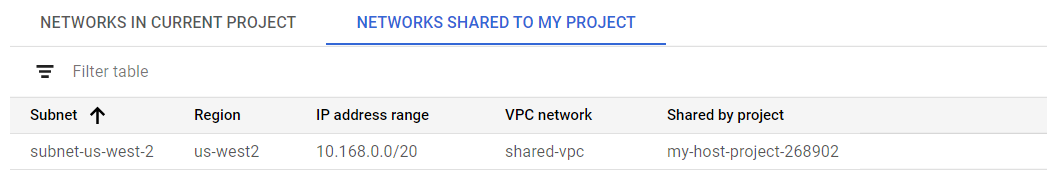
The problem is that not all regions support AI Platform Notebooks instance service and a Shared VPC usually does not contain all regions. For example, the following picture shows my shared VPC (subnet-us-west-2) from my host project (my-host-project-268902) only has region us-west2. For security reason, the shared VPC has turned the Private Google Access on, which means all VMs created in my service project can not have public IP.
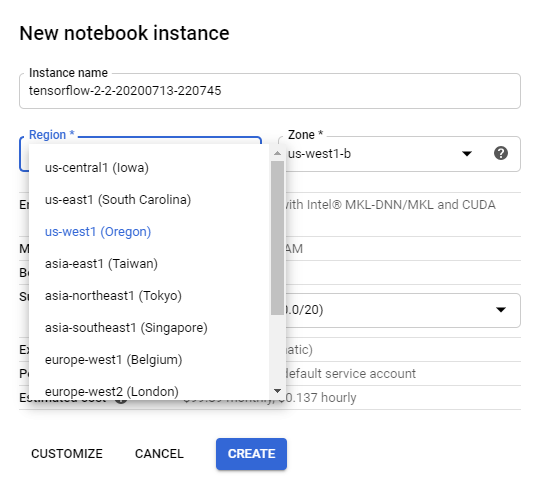
As shown by the following picture, however, if you create the AI Platform Notebooks instance through the web console, you would find that there is no us-west2 in the Region dropdown list. Now, I need to create a notebook instance in region us-west2 to use my shared VPC to connect to other network resources. What should I do?
If you are familiar with GCP, you might know that I can create an AI platform notebooks instance from the gcloud beta notebooks instance create command line as described in Create an AI Platform Notebooks instance from the command line. However, when I specified the subnet to the shared VPC, I got the PERMISSION_DENIED error message shown as below:

How Did I Solve The Problem?
Instead of using the above gcloud beta notebooks instance create command, I created a Deep Learning VM instance from the command gcloud compute instances create as described in Create a TensorFlow Deep Learning VM instance from the command line. However, the example command in the document can create a Deep Learning VM, but it did not show up in the AI Platform Notebooks Instance page.
The following are the two commands that I have adapted from the Deep Learning VM command mentioned above to create AI Platform Notebooks instances without GPUs and with GPUs.
Command to create an instance without GPUs (cpu command)
export IMAGE_FAMILY="tf2-ent-latest-cpu"
export ZONE="us-west2-a"
export INSTANCE_NAME="cpu-instance-test"
export INSTANCE_TYPE="n1-standard-4"
export SUBNETWORK="https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/my-host-project-268902/regions/us-west2/subnetworks/subnet-us-west-2"
export PROJECT_ID="my-service-project-271521"
gcloud compute instances create $INSTANCE_NAME \
--zone=$ZONE \
--project=$PROJECT_ID \
--machine-type=$INSTANCE_TYPE \
--image-family=$IMAGE_FAMILY \
--image-project=deeplearning-platform-release \
--subnet=$SUBNETWORK \
--no-address \
--tags=deeplearning-vm \
--scopes=https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform \
--metadata='proxy-mode=project_editors'
Here is a breakdown of the command, so you understand what is happening:
gcloud compute instances createcreates a new instance with specified name--zonespecifies which zone the instance to be created and needs to be consistent to the shared VPC region--projectspecifies the ID of project where the instance to be created--machine-typespecifies the machine type as n1-standard-4, which provides 4 vCPU and 15GB of RAM. For more machine types, see GCP VM Machine Types--image-familyspecifies the Deep Learning VM image. For more image families, see AI Platform Deep Learning VM Images--image-projectmust bedeeplearning-platform-release--subnetspecifies the shared subnet from the host project--no-addressspecifies that the VM has no public address. It can be ignored, if the shared VPC allows public IP--tagsmust bedeeplearning-vm, otherwise, it will not show up in the notebook instance page--scopesand--metadatamust be specified as above, otherwise, the instance cannot set up the proxy to the JupyterLab and the link of OPEN JUPYTERLAB won’t work. For more information of the settings, see Use SSH to Access to JupyterLab.
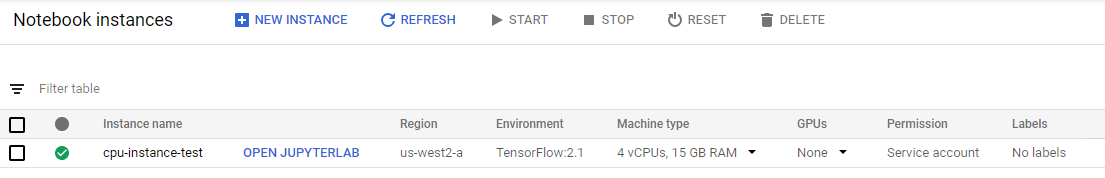
With success of above command, an instance named cpu-instance-test can be seen from the AI Platform Notebook Instances page:
Command to create an instance with GPUs (gpu command)
export IMAGE_FAMILY="tf2-ent-latest-gpu"
export ZONE="us-west2-b"
export INSTANCE_NAME="gpu-instance-test"
export INSTANCE_TYPE="n1-standard-4"
export SUBNETWORK="https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/my-host-project-268902/regions/us-west2/subnetworks/subnet-us-west-2"
export PROJECT_ID="my-service-project-271521"
gcloud compute instances create $INSTANCE_NAME \
--zone=$ZONE \
--project=$PROJECT_ID \
--machine-type=$INSTANCE_TYPE \
--image-family=$IMAGE_FAMILY \
--image-project=deeplearning-platform-release \
--subnet=$SUBNETWORK \
--no-address \
--tags=deeplearning-vm \
--scopes=https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform \
--maintenance-policy=TERMINATE \
--accelerator="type=nvidia-tesla-p4,count=1" \
--metadata='install-nvidia-driver=True,proxy-mode=project_editors'
The gpu command is similar to the cpu command, the only differences are the last three options:
--maintenance-policymust beTERMINATE, because of the GPU restrictions--acceleratorspecifies the GPU type to use. For more details of GPU types, see Create GPU instance gcloud--metadatainstall-nvidia-driver=Truespecifies that the NVIDIA driver should be installed andproxy-mode=project_editorsis used to setup proxy to JupyterLab.
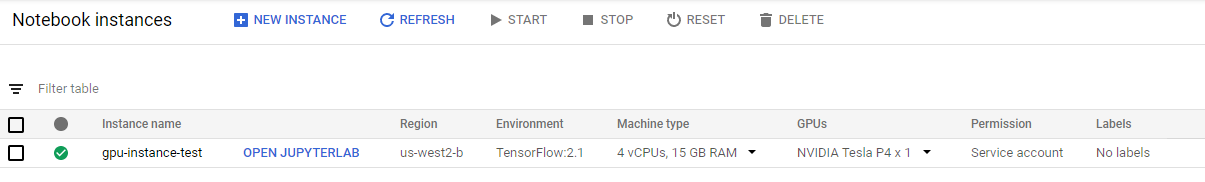
With the success of above command, an instance with name of gpu-instance-test will show in the Notebook instances page:
I hope this post is helpful. If I missed anything, please let me know in the comments.
References
Create an AI Platform Notebooks instance from the command line
Create a TensorFlow Deep Learning VM instance from the command line