Google Cloud Dataflow is a fully managed platform running Apache Beam for unified stream and batch data processing services. With its fully managed approach on resource provisioning and horizontal autoscaling, you have access to virtually unlimited capacity and optimized price-to-performance to solve your data pipeline processing challenges.
Shared Virtual Private Network (VPC) allows an organization to connect resources from multiple projects to a common VPC network. This allows cloud resources to communicate with each other securely and efficiently using internal IP addresses from that network. When you use shared VPC, you designates a project as a Host Project and attach one or more Service Projects to it. The common VPC network shared accross the Host and Service projects is called Shared VPC Network. Using Shared VPC is a good practice for Organization Admins to keep centralized control over network resources, while delegating administrative responsibilities to Service Project Admins.
Dataflow regional endpoints store and handle metadata about Dataflow jobs, and deploy and control Dataflow workers. However, Dataflow regional endpoints are not yet available in all Google Cloud regions.
If the Shared VPC does not have any subnet in the region that provides the Dataflow regional endpoints, you need a tricky way to run your Dataflow jobs. In addition, because Dataflow service needs to use the network shared by the host project, there are some neccesary consigurations need to be set up on both Host and Serive projects. This post describes these steps and settings to run a Dataflow sample WordCount job in a Shared VPC that does not have any Dataflow regional endpoints.
Table of Content
- Table of Content
- Organization and Shared VPC
- Settings in Host Project
- Settings in Service Project
- Specifying Execution Paramters
- References
Organization and Shared VPC
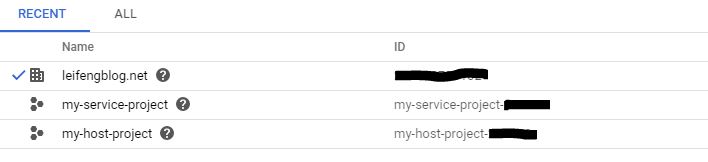
The organization structure used in the experiment is shown in the following table. The Organization node(leifengblog.net) has two projects: my-service-project is the Service Project where the Dataflow job runs, and my-host-project is the Host Project that hosts the shared VPC.
For the best practice, the Organiztion Admin has setup the following constraints in the Organization Policies page under the organization’s IAM & Admin menu.
| Constraint | Configuration | Exaplanation |
|---|---|---|
Define allowed external IPs for VM instances |
Set Policy values to Deny All |
All VM instances are not allowed to use external IP address |
Skip default network creation |
Pick Customize and turn on Enforcement |
Don’t create default network when create a new project |
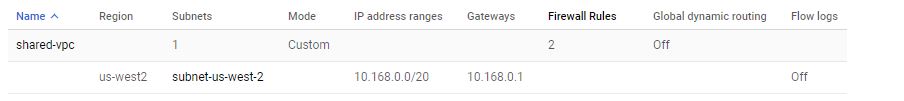
The following table shows the Shared VPC from the Host Project. There is only one subnet in region us-west2 with Private Google Access on. Unfortunately, there is no Dataflow regional endpoint available in the region us-west2.
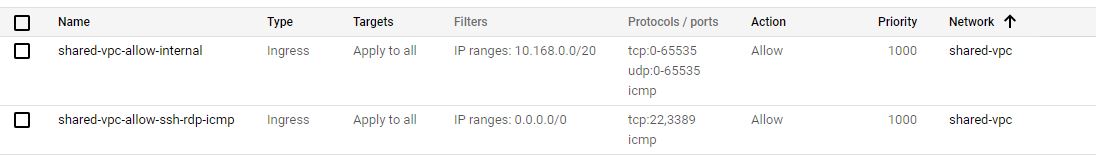
In addition, the following firewalls are applied to all instances in the shared VPC networks.
Settings in Host Project
The following settings might need the role of Shared VPC Admin or Network Admin from the Organization or Host Project:
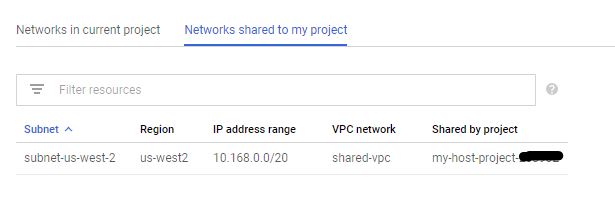
- Add the user account or user group that runs Dataflow in the Service Project to the shared VPC with
Compute Network Userrole, otherwise, the user/group cannot see theNetwork shared to my projecttab on theVPC networkpage in the Service project. See below for an example.
- Add the Dataflow service account from the Service Project, in the format of
service-<SERVICE_PROJECT_NUMBER>@dataflow-service-producer-prod.iam.gserviceaccount.com, to the shared subnet with theCompute Network Userrole. The Dataflow service account would be created once you enable the Dataflow API, which is one of the settings in Service Project below.
Note: Depending on which mode (e.g. project permission or individual subnet permission) you are using to share the VPC, you need to make sure the Dataflow account from the Service project has the Compute Network User role in the shared Subnet.
Settings in Service Project
The following settings might need the role of Owner or Editor from the Service Project:
-
Enbale the Cloud Dataflow, Compute Engine, and Cloud Storage APIs. After the Cloud Dataflow API is enbaled, the Cloud Dataflow Service Account with format of
service-<PROJECT_NUMBER>@dataflow-service-producer-prod.iam.gserviceaccount.comshould be created. Now you can contact the shared VPC admin or Host Project Owner to add the Dataflow service account to the shared VPC withCompute Network Userrole. -
In the IAM & admin page, make sure that
1) the Cloud Dataflow Service Account has a role of
Cloud Dataflow Service Agent, or you can run the following command to add it:gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding [PROJECT-ID] \ --member serviceAccount: service-[PROJECT-NUMBER]@dataflow-service-producer-prod.iam.gserviceaccount.com \ --role roles/dataflow.serviceAgent2) the Compute Engine Service Agent has roles of
Compute Network UserandCompute Engine Service Agent. Otherwise, use the following command to add them:gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding [PROJECT-ID] \ --member serviceAccount: service-[PROJECT-NUMBER]@ compute-system.iam.gserviceaccount.com \ --role roles/compute.networkUser \ --role roles/compute.serviceAgent -
Create authentication key file following the process described in set up authentication:
a. From Cloud Console go to IAM & Admin page, and then Service Accouts
b. From the page select New service account
c. Enter a name for the Service account name and select Project > Owner as the Role
d. Click Create. Save the JSON file that contains your key to your local folder.
You will need the the path of the file to set the environment variable GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS in the following scripts.
Specifying Execution Paramters
This section describes the settings for Java SDK 2.x and Python 3.x. Check the quickstarts for more information.
Java and Maven
If you use Java and Apache Maven, you need to run the following command to create the Maven project containing the Apache Beam WordCount source code.
$ mvn archetype:generate \
-DarchetypeGroupId=org.apache.beam \
-DarchetypeArtifactId=beam-sdks-java-maven-archetypes-examples \
-DarchetypeVersion=2.19.0 \
-DgroupId=org.example \
-DartifactId=word-count-beam \
-Dversion="0.1" \
-Dpackage=org.apache.beam.examples \
-DinteractiveMode=false \
-Dhttp.proxyHost=[YOUR-PROXY-HOST]
-Dhttp.proxyPort=[YOUR-PROXY-PORT]
-Dhttps.proxyHost=[YOUR-PROXY-HOST]
-Dhttps.proxyPort=[YOUR-PROXY-PORT]
Note: you need the last four lines only if you are behind a proxy, otherwise, feel free to skip them.
Once the Maven project created, you can use the following scripts to run the Apache Beam job on Dataflow:
# load the application credential file
export GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS="[path-to-authentication-key-file]"
echo $GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS
# submit job
mvn -Pdataflow-runner compile exec:java \
-Dexec.mainClass=org.apache.beam.examples.WordCount \
-Dhttp.proxyHost=[YOUR-PROXY-HOST] \
-Dhttp.proxyPort=[YOUR-PROXY-PORT] \
-Dhttps.proxyHost=[YOUR-PROXY-HOST] \
-Dhttps.proxyPort=[YOUR-PROXY-PORT] \
-Dexec.args="--project=[SERVICE_PROJECT_ID] \
--stagingLocation=gs://[CLOUD_STORAGE_BUCKET]/staging/ \
--output=gs://[CLOUD_STORAGE_BUCKET]/output/ \
--gcpTempLocation=gs://[CLOUD_STORAGE_BUCKET]/temp/ \
--runner=DataflowRunner \
--usePublicIps=false \
--region=us-west1 \
--zone=us-us-west2-a \
--subnetwork=https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/[HOST_PROJECT_ID]/regions/us-west2/subnetworks/subnet-us-west-2"
Please refer to the document of Specifying execution parameters for detailed explanation on each of the parameters. I would list a few points worth highlighting here:
- For the [SERVICE_PROJECT-ID] and [HOST_PROJECT_ID], make sure to use the project id’s, rather than the project names.
- The
subnetworkis the shared subnet comes from the host project. Because there is no Dataflow regional endpoint in regionus-west2, it needs to specify theregiontous-west1or any other regions that have the Dataflow regional endpoint. But it still needs to set thezoneto one of the zones inus-west2. - Don’t forget the parameter
--usePublicIps=false, if your organization don’t allow to use external IP address.
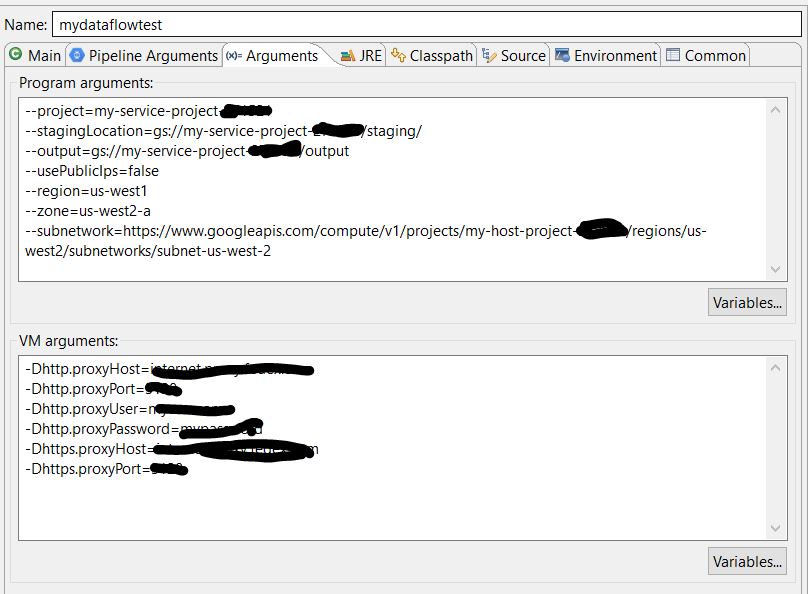
Java and Eclipse
If you would use Eclipse, you can set the above parameters in the Arguments tab of Run Configurations, see below for an example:
Python
If you use Python, use the following settings to run the dataflow job in the Service Project decribed in this post.
export GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS="[path-to-authentication-key-file]"
echo $GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS
PROJECT=[SERVICE_PROJECT_ID]
BUCKET=gs://[CLOUD_STORAGE_BUCKET]
python -m apache_beam.examples.wordcount \
--input gs://dataflow-samples/shakespeare/kinglear.txt \
--output $BUCKET/outputs \
--temp_location $BUCKET/tmp \
--runner DataflowRunner \
--project $PROJECT \
--region 'us-west1' \
--no_use_public_ips True \
--subnetwork 'https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/[HOST_PROJECT_ID]/regions/us-west2/subnetworks/subnet-us-west-2'
I hope this post is helpful. If I missed anything, please let me know in the comments.
References
https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/guides/specifying-networks
https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/concepts/security-and-permissions#cloud-dataflow-service-account
https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/guides/routes-firewall
https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/concepts/regional-endpoints
https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/guides/specifying-exec-params