Connecting to an Oracle Database with Python cx_Oracle through LDAP is not trivial. It needs to install cx_Oracle module and Oracle Instant Client libraries, as well as set up LDAP settings in the Oracle Client. This post describes the processes to set up a connection to an Oracle Database on-premises with Python on a Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Virtual Machine in Microsoft Azure.
Connection Architecture
The following picture depicts the connection architcture. Users can run a Python program that calls the cx_Oracle module that loads Oracle Client libraries. The libraries provide necessary network connectivity to access to an Oracle Database instance. Thus, to connect to a remote Oracle Database, it needs to install both cx_Oracle moduel and Oracle Client libraries.
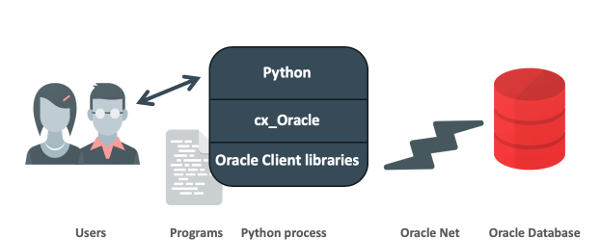
Picture comes from (cx_Oracle Architecture)
Install cx_Oracle
- Check your Python versions through the following commands to make sure you have Python 3 installed. All the following steps are for Python 3:
python --version python3 --version - Before installing cx_Oracle, you might need to install
pip3for Python 3 through the following commands:sudo apt update && sudo apt install python3-pip - With
pip3installed, you can run the following command to install cx_Oracle:pip3 install cx_Oracle
Install Oracle Client
There are multiple ways to install the Oracle Cient, the following describes the steps to install an Oracle Instant Client through zip file.
-
Download the latest version “Basic” or “Basic Light” zip file from the Instant Client download page64-bit or 32-bit.
- Unzip the package into a single directory that is accessible. For example:
sudo mkdir -p /opt/oracle sudo unzip instantclient-basic-linux.x64-21.1.0.0.0.zip -d /opt/oracle/ - Install
libaiopackage. This package is also calledlibaio1in some distributions. For example, in my case, I need to run:sudo apt install libaio1 - Add the following line in the
$HOME/.bashrcfile and runsource .bashrcto refresh the settings:export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/oracle/instantclient_21_1 - Create subdirectory
network/adminwithin the directoryopt/oracle/instantclient_21_1/, if it is not created yet. -
In the
network/adminsubdirectory, create two files:1.
sqlnet.orawith the content:# sqlnet.ora # Place this file in the network/admin subdirectory or your # $LD_LIBRARY_PATH location. NAMES.DIRECTORY_PATH = (LDAP)2.
ldap.orawith the content:# ldap.ora # Place this file in the network/admin subdirectory or your # $LD_LIBRARY_PATH location. DIRECTORY_SERVERS = ([ldapservername:ldapport]) DEFAULT_ADMIN_CONTEXT = "[DomainContext]" DIRECTORY_SERVER_TYPE = OID
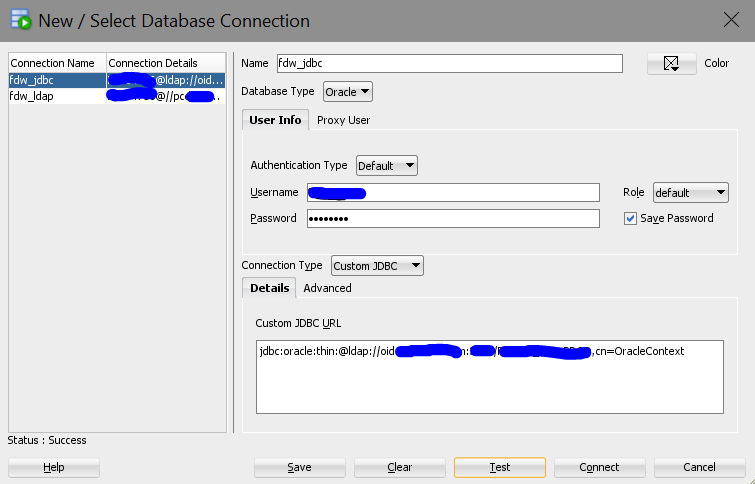
Note: you need to update the content in the square brackets with your own information. The following picture shows an example of Custom JDBC connection to an Oracle Database in SQL Developer.
The conncetion string in the Custom JDBC URL box usually has the format below. This is where you can get the information in the brackets.
jdbc:oracle:thin:@ldap://[ldapservername:ldapport]/[DBservicename],[DomainContext]
Connect to Oracle Database in Python Programs
With the installation and setttings, the following Python scripts is an example program that can be used to connect to a remote Oracle Database.
Althrough the scripts itself is pretty simple and self-explanatory, you need to note the [DBservicename] in the scripts. If your OID is created with only one context of cn=OracleContext, then you need to append a dot (.) at the end of service name. For my case, my service name is ABC_DEFG and the OID is created with the only context of cn=OracleContext, so I need to specify the server as ABC_DEFG..
'''
A Python scripts that:
1) get the username and password for the oracle database;
2) read sql query from a file
3) run the query and print out column metadata
'''
import cx_Oracle
import getpass # library to input password
try:
# input username and password
username = input("Please enter your FDW username: ")
password = getpass.getpass("Enter your LDAP password: ")
# read sql query from file
sqlfilename = "./my_sql_query.sql"
f = open(sqlfilename)
sql_string = f.read()
print("SQL = " + sql_string)
# set up connection through LDAP
con = cx_Oracle.connect('{0}/{1}@[DBservicename][.]'.format(username, password))
# create a cursor instance
cursor = con.cursor()
# run the query
cursor.execute(sql_string)
# print out metadata
for column in cursor.description:
print(column)
except cx_Oracle.DatabaseError as e:
print("There is a problem with Oracle", e)
finally:
if cursor:
cursor.close()
if con:
con.close()
I hope this post is helpful. If I missed anything, please let me know in the comments.
References
cx_Oracle 8 Installation Document: https://cx-oracle.readthedocs.io/en/latest/user_guide/installation.html#install-oracle-client
Connecting Python to Oracle Databases with cx_Oracle and ldap: https://eikonomega.medium.com/connecting-to-oracle-database-with-cx-oracle-and-ldap-5da7925a305c