With the rapid influx of new LLM research papers, I wanted a way to store, summarize, and explore these findings seamlessly. The idea was to build a QnA system that could quickly retrieve relevant knowledge while keeping everything under my control. Given the excitement around DeepSeek R1, I thought this as a perfect opportunity to test its capabilities. In this blog, I’ll share how I set up a local Knowledge QnA system using Ollama, DeepSeek R1, and AnythingLLM—a solution that enables efficient querying of structured and unstructured knowledge sources while maintaining full data privacy and local execution.
Why a Local QnA System?
As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly powerful, many businesses and developers seek ways to leverage them for internal knowledge retrieval. However, using cloud-based APIs raises concerns about data privacy, cost, and dependency on external services. By setting up a local QnA system, you get:
- Full control over your data with no external API calls
- Lower cost compared to SaaS-based LLM APIs
- Faster response times for internal queries
With that in mind, I chose Ollama to run the distilled version of DeepSeek R1 locally and AnythingLLM as an interface to manage knowledge ingestion and retrieval.
Step 1: Setting Up Ollama
Ollama is a lightweight framework that allows you to run open-source LLMs locally. It simplifies model management and execution without requiring complex setup.
Installing Ollama
-
Go to the Ollama website (https://ollama.com/) and download the appropriate version for your operating system.
-
Once downloaded, unzip the file and double-click to install.
-
After installation, verify it’s working by running the following command in terminal:
ollama --version
If installed correctly, this will display the version number.
You can also check Ollama’s status by opening http://localhost:11434 in a web browser, which will return the status of the installed Ollama.
Installing DeepSeek R1
-
Visit the Models section on Ollama’s website.
-
Search for DeepSeek R1 and choose the version you want to download. In this guide, I downloaded the 7B model.
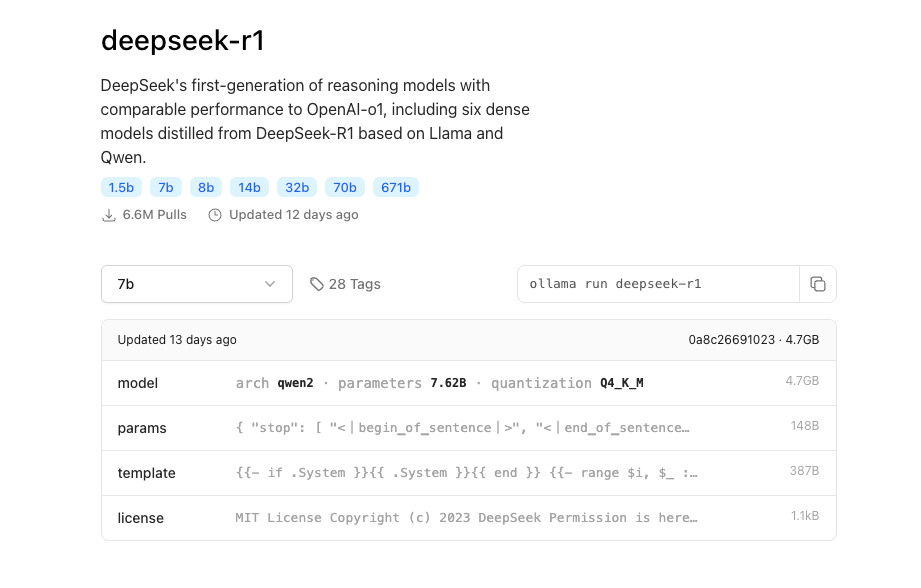
- Copy and run the following command in the terminal to download the model:
ollama run deepseek-r1:7b
- Once the installation is complete, you can test it with a simple prompt:
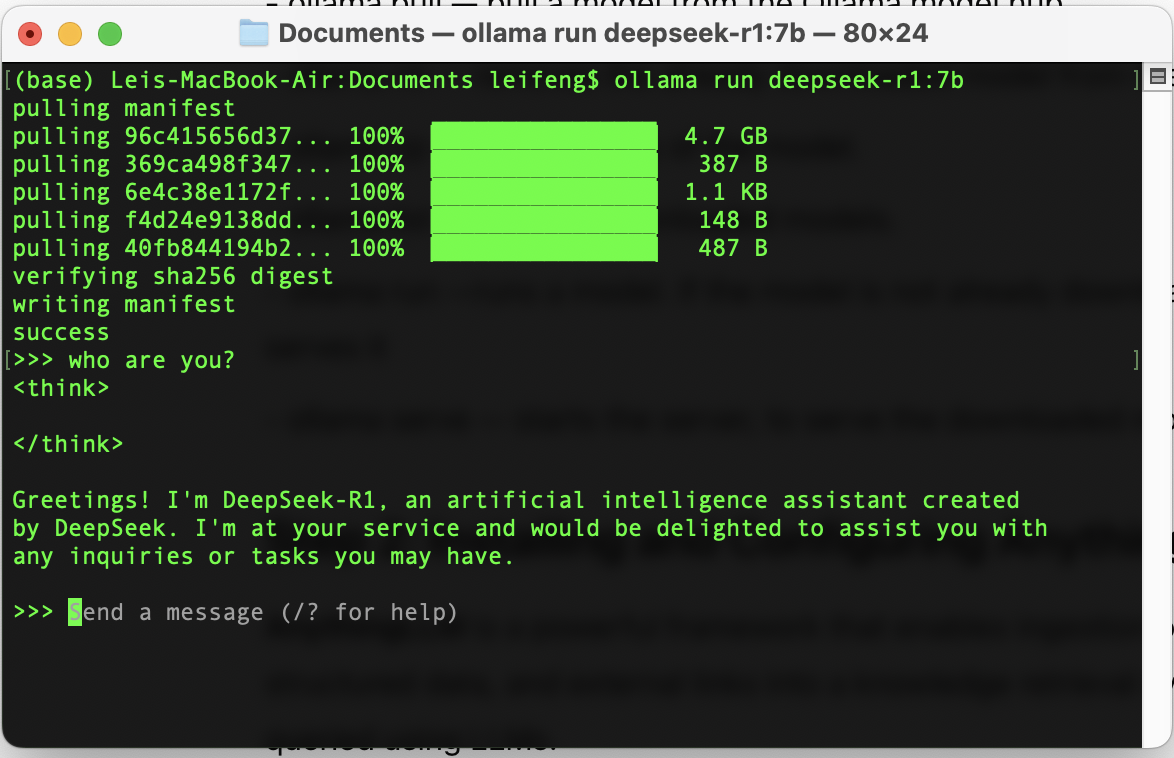
To exit, press Ctrl + D, or type /bye or /exit.
Useful Quick-start Ollama Commands
ollama pull— Pulls a model from the Ollama model hub.ollama rm— Removes the downloaded model from the local computer.ollama cp— Makes a copy of the model.ollama list— Lists the downloaded models.ollama run— Runs a model. If not downloaded, it pulls and serves it.ollama serve— Starts the server to serve the downloaded models.
Step 2: Installing and Configuring AnythingLLM
AnythingLLM is a powerful framework that enables ingestion of documents, structured data, and external links into a knowledge retrieval system that can be queried using LLMs.
Installing AnythingLLM
-
Visit the AnythingLLM website and download the desktop version.
-
Install the software and launch it.
-
When prompted, click Get Started.
-
In the LLM Prference, select Ollama as the LLM provider.
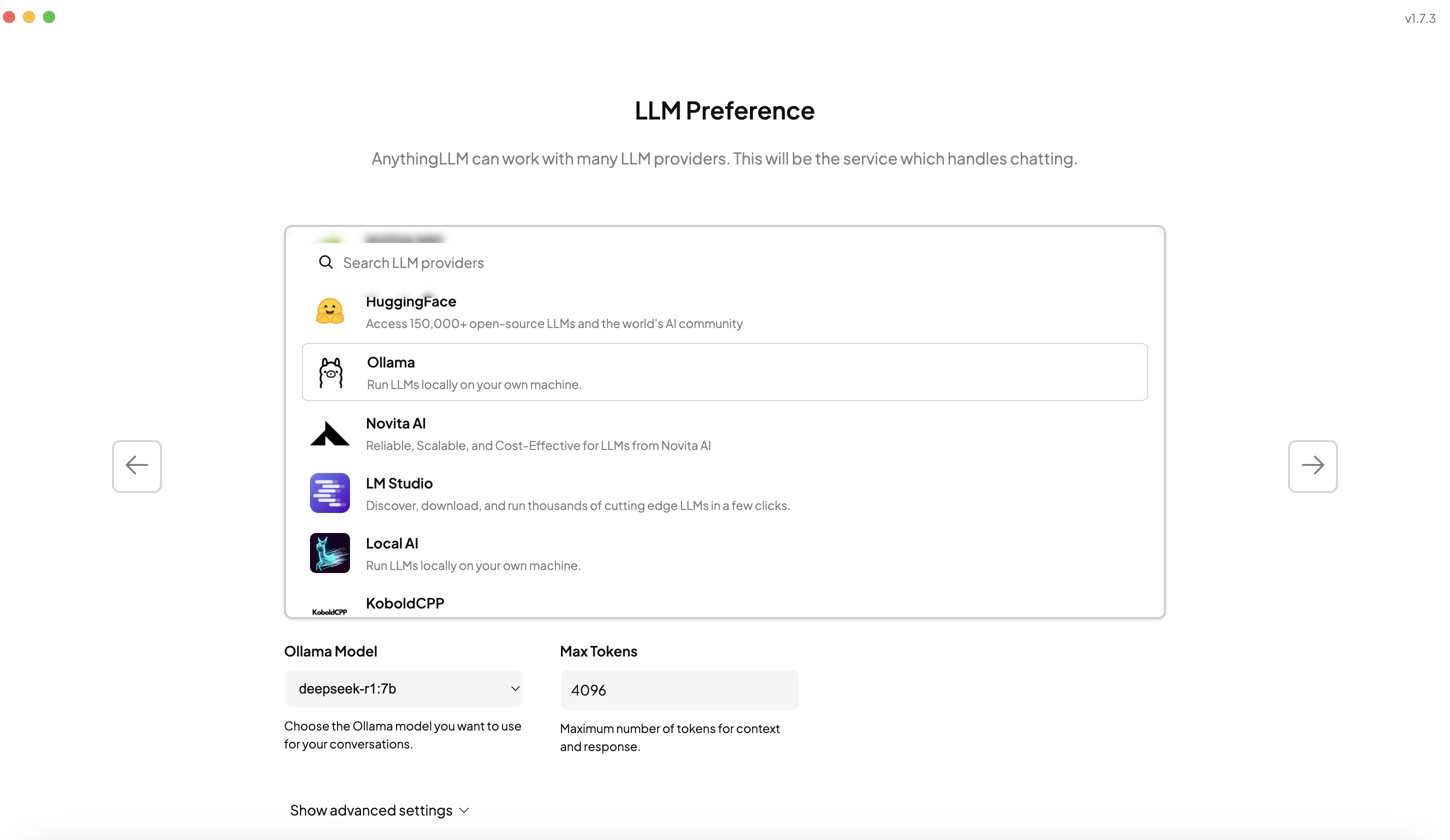
-
Proceed with the default settings until you reach the page for workspace creation.
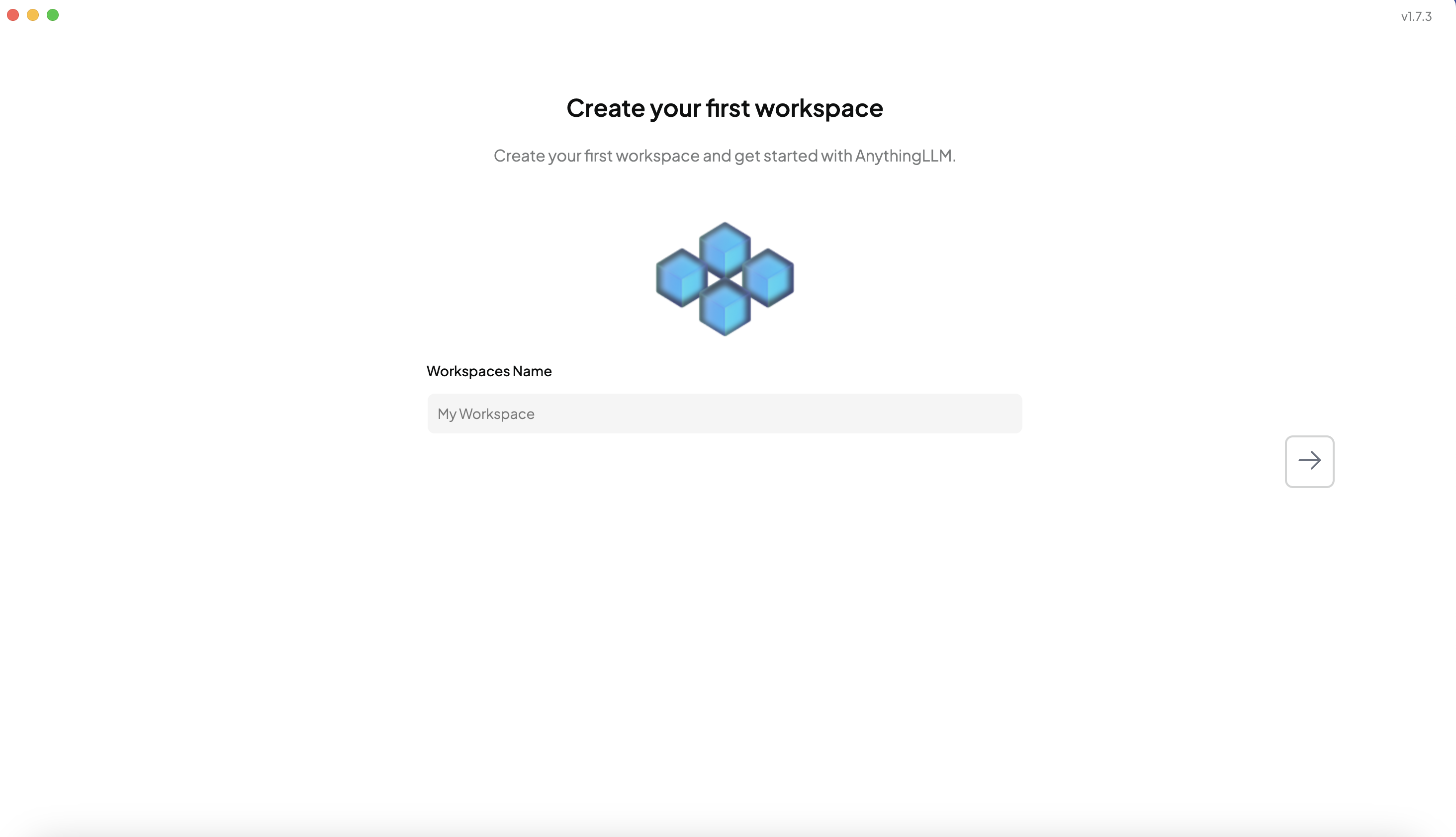
-
Name your workspace and finalize the setup.
Once configured, click your workspace name on the left pane to test the chatbot. You should see DeepSeek R1 processing queries.
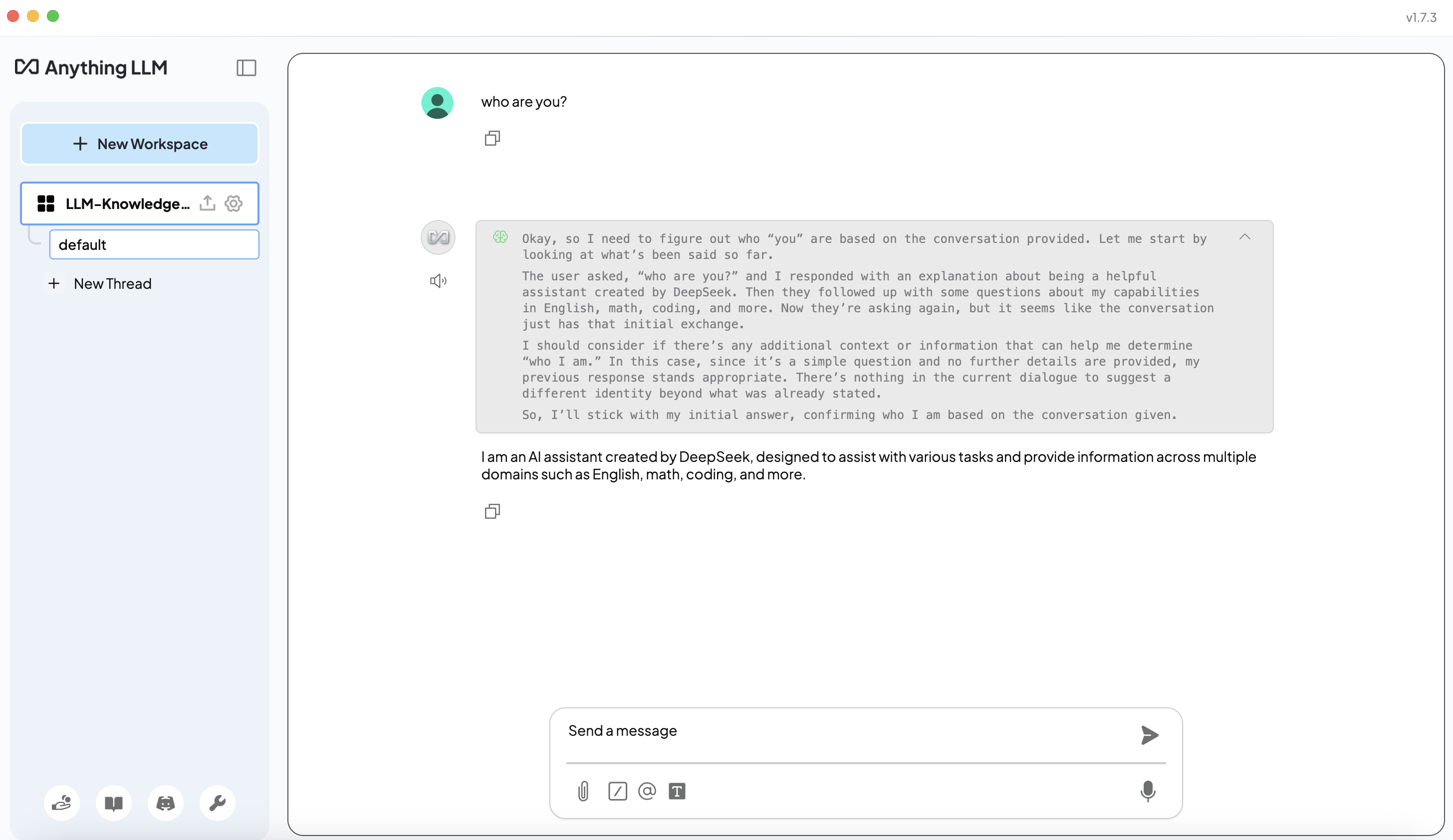
Step 3: Ingesting Knowledge Sources
AnythingLLM allows you to upload PDFs, Markdown, JSON, and audio files as knowledge sources. Here’s how you can start adding documents:
-
Click the Upload button next to the workspace name.
-
From the file upload UI, select and upload your documents.
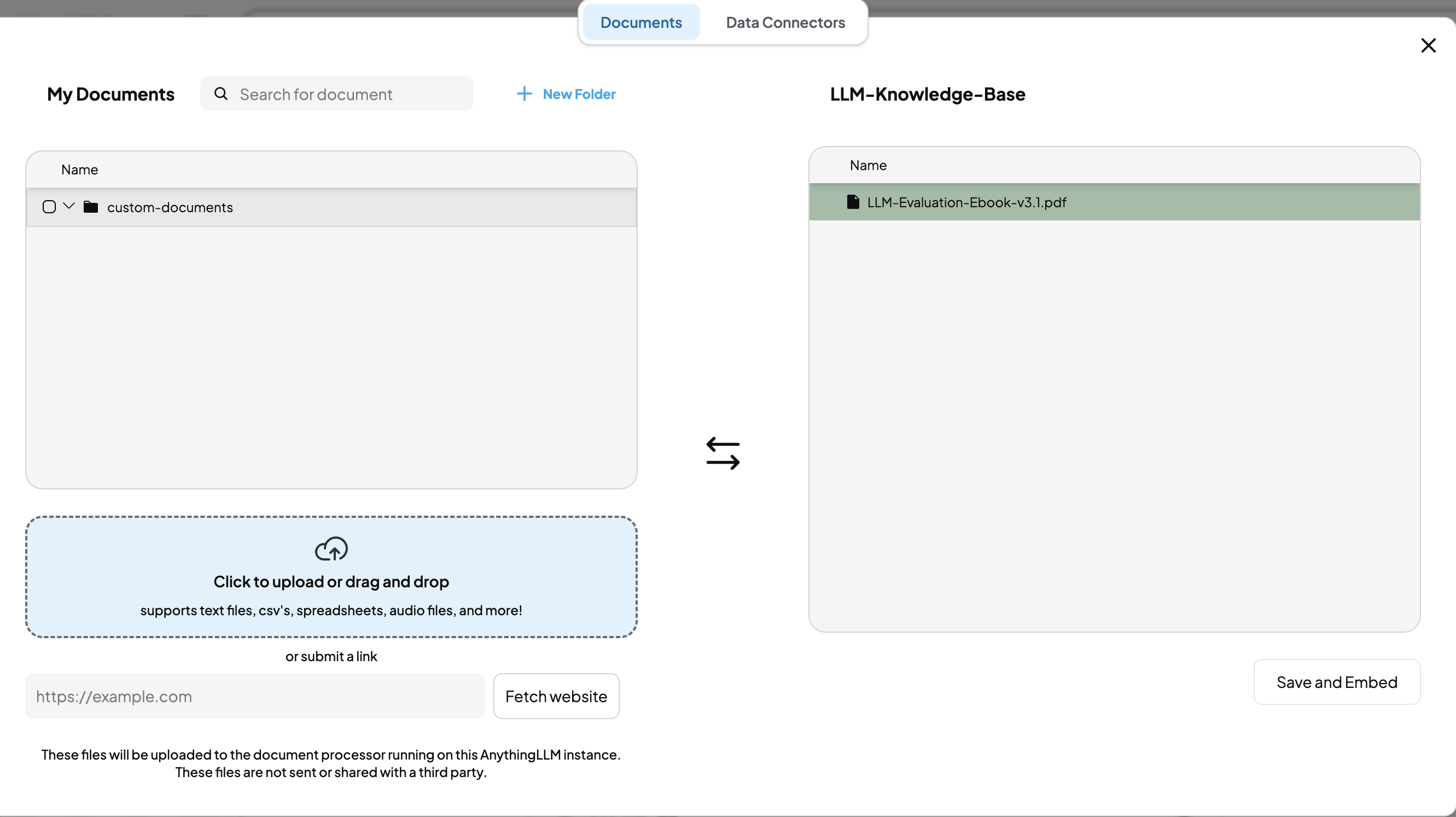
-
Choose the document to add to the workspace.
-
Save it as embeddings for retrieval.
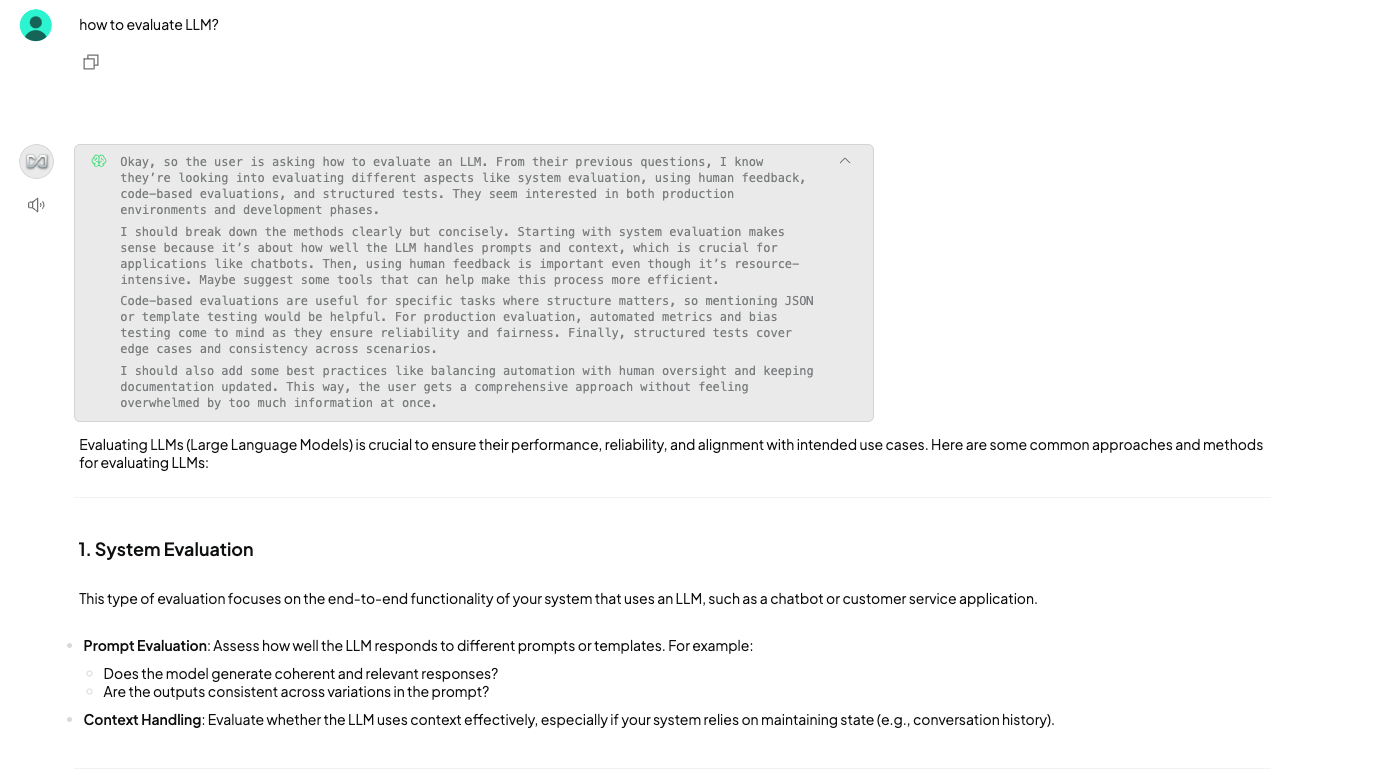
Once the knowledge base is set up, you can query it using the AnythingLLM UI. For example, I tested the system with the question: “How do you evaluate an LLM?”
The response included the most relevant answer based on the ingested data.

Conclusion
By combining Ollama, DeepSeek R1, and AnythingLLM, I successfully set up a local QnA system that:
- Runs entirely on local hardware
- Supports document-based knowledge retrieval
- Maintains full data privacy
- Eliminates reliance on cloud APIs
This setup is ideal for businesses, teams, and individuals who need fast, private, and cost-effective knowledge retrieval.
Future Enhancements
- Integrating vector databases like ChromaDB for improved retrieval.
- Automating document ingestion using CRON jobs.
- Fine-tuning DeepSeek R1 for domain-specific queries.
I hope this guide helps you in setting up your own local QnA system! Feel free to share your experiences or ask any questions in the comments.